Applications of Second and Third Laws
Applications of Second and Third Laws: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Free Fall of Bodies, Contact Forces, Motion of Connected Bodies, Motion on Inclined Plane, Weightlessness, Weight in a Lift with No Acceleration, Weight in a Lift Accelerating Upwards, etc.
Important Questions on Applications of Second and Third Laws
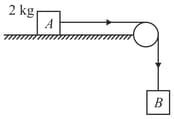
The coefficient of static friction, , between block of mass and the table as shown in the figure is . What would be the maximum mass value of block so that, the two blocks do not move? The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless .
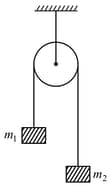
Two blocks are hung vertically over a light frictionless pulley as shown here. What is the acceleration of the masses when they are left free?
A block has been placed on an inclined plane with the slope angle block slides down the plane at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is equal to :
A ball is dropped from a high rise platform at, starting from rest. After another ball is thrown downwards from the same platform with the speed . The two balls meet at, . What is the value of ? (Take, )
Two bodies, (of mass ) and (of mass ), are dropped from heights of and , respectively. The ratio of the times taken by them to reach the ground is
A body falling freely from a given height hits an inclined plane in its path at a height . As a result of this impact, the direction of the velocity of the body becomes horizontal. For what value of the body will take maximum time to reach the ground?
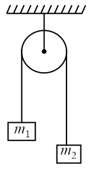
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (vertically). If the acceleration of the system is , then the ratio of the masses is –
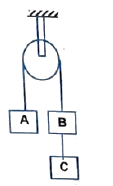
Two masses and tied to a string are hanging over a light frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses when left free to move? ( )
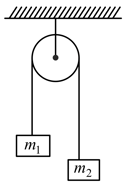
Two masses and tied to a string are hanging over a light frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses when left free to move? ( )
A particle starts sliding down a frictionless inclined plane. If is the distance travelled by it from time to , the ratio is
A block of mass is lying on a smooth inclined plane as shown in the figure.The tension in the string will be (string is light and )
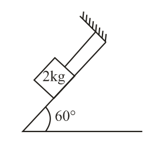
A horizontal force pulls three masses , and , lying on a frictionless table and connected by light strings. Find the tension in the string between blocks and .
What is better to have one pulley or multiple pulleys?
Two masses 2 kg and 3 kg are attached to the end of the string passed over a pulley fixed at the top. Find acceleration of the blocks?
What happens when you put multiple pulleys together?
In a pulley block system,tension in a massless string is same at all points.
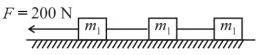
Three equal weights of mass 2 kg each are hanging on a string passing over a fixed pulley as shown in the figure. What is the tension in the string connecting weights B and C ?
Starting from rest, a body slides down a 45° inclined plane in twice the time it takes to slide down the same distance in the absence of friction. The coefficient of friction between the body and the inclined plane is
Two blocks A and B of equal masses are in contact initially. The coefficients of friction between the inclined plane and the surface of A and B are respectively. The blocks will remain in contact and will fall with common acceleration_____
Why Crowning of pulley is done?
